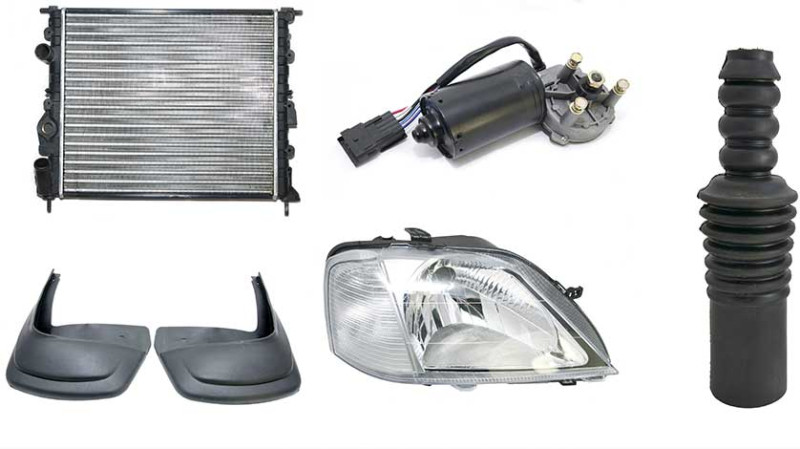
Whether you're a DIY enthusiast working on your own vehicle, a young professional looking to deepen your automotive knowledge, or a seasoned tradesman who wants to communicate clearly with clients and suppliers, understanding the parts of a car can be extremely valuable. In this guide, we'll introduce you to the fundamental components of a car, helping you grasp the vocabulary, functionality, and importance of each part. This article is especially useful if you live in the United Kingdom and want to be more confident discussing vehicles, whether casually or professionally.
Exterior Car Parts
The exterior of a car is the first thing you notice. It not only defines the vehicle's style but also serves functional purposes like aerodynamics and protection. Learning the names and purposes of different exterior components will help you better maintain your vehicle and articulate issues to a mechanic.
Body Panels: These include doors, bonnets (the UK term for 'hoods'), roofs, and fenders. They're typically made of metal or composites and are essential for protecting the interior of the vehicle as well as offering structural integrity.
Bumper: Located at the front and rear, the bumper absorbs minor impacts and can prevent more serious damage during minor collisions.
Headlights and Taillights: Headlights illuminate the road ahead during night driving, while taillights ensure vehicles behind you can see your position clearly. Daytime Running Lights (DRLs) and fog lamps are also essential lighting parts.
Windscreen and Windows: Vital for visibility and passenger protection. Advances in glass technology have introduced features like UV protection, heating elements for defrosting, and soundproofing.
Mirrors: Essential for safe driving, side mirrors and rearview mirrors assist in manoeuvering, reversing, and monitoring surrounding traffic.
Interior Car Parts
While the car’s exterior protects and presents, the interior provides comfort, control, and communication between driver and machine. Understanding interior parts is essential for both maintenance and upgrading your driving experience.
Dashboard: Houses critical information displays such as speedometers, fuel gauges, and now digital interfaces like infotainment systems and touchscreens.
Seats: Car seats now come with varying degrees of adjustability, lumbar support, and heating/cooling features, all designed for maximum comfort and safety.
Steering Wheel: Beyond simply directing the car, modern steering wheels often incorporate multimedia controls, cruise control buttons, and even heating elements.
Pedals: In manual transmission vehicles, you'll find three: clutch, brake, and accelerator, while automatic cars will only have brake and accelerator pedals.
Gear Stick: Used to change gears. In automatic vehicles, this is often simpler, but manual vehicles give drivers greater control over engine performance.
Under the Bonnet: Engine and Mechanical Parts
Looking under the bonnet can be intimidating, but understanding the basics of what’s going on beneath will dramatically improve your car literacy. These parts are the powerhouse components that keep your vehicle moving.
Engine: Often referred to as the heart of the car, the engine converts fuel into movement. Engines vary from small three-cylinder configurations to powerful V8s and advanced hybrid systems.
Battery: Powers all electrical components when the engine is off and helps to start the car. Regular maintenance like cleaning the terminals can prevent common issues.
Radiator: Keeps the engine cool by circulating coolant through the engine and dissipating heat via airflow when driving or using the fan when stationary.
Alternator: Once the car is running, the alternator generates electricity to recharge the battery and power the electrical systems.
Air Filter: Ensures that only clean, debris-free air enters the engine, enhancing fuel efficiency and engine life.
Suspension and Brake System
The suspension and braking systems are vital for safety, comfort, and overall driving quality. Without a working understanding of these systems, diagnosing car issues can be challenging.
Shock Absorbers and Springs: These parts absorb bumps and road irregularities, giving you a smoother ride and better vehicle control.
Brakes: Including brake pads, rotors (discs), and calipers. Modern cars commonly use disc brakes for their superior stopping power, with Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) ensuring optimal performance during sudden stops.
Steering System: The steering system, including the rack and pinion mechanisms or electric power-assisted steering, allows drivers to control vehicle direction effectively and efficiently.
Wheels and Tyres
No matter how powerful your car is, it connects to the road through four critical points - the tyres. Understanding your wheels and tyres can dramatically improve driving safety and fuel efficiency.
Tyres: Available in various types like summer, winter, and all-season versions. Tyres must meet British safety standards, including the recommended tread depth of at least 1.6mm.
Rims: The metal part onto which the tyre is mounted. Rims can be simple steel models or stylish alloys that add both flair and function to a vehicle.
Wheel Alignment and Balancing: Regular wheel maintenance ensures the car handles properly and prevents uneven tyre wear, saving you money in the long run.
Common Car Parts Vocabulary Table
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Bonnet | Protects the engine compartment and allows access for servicing |
| Boot | The rear storage compartment of the car |
| Chassis | The vehicle's frame that supports all components |
| Exhaust System | Channels emissions away from the vehicle and reduces pollution |
| Fuel Tank | Stores petrol or diesel used by the engine |
| Transmission | Transmits power from the engine to the wheels |
| Windshield Wipers | Clear rain and debris from the windscreen for better visibility |
Tips for Learning Car Parts Faster
Mastering auto parts vocabulary doesn't happen overnight. A good strategy is to engage actively with your car - pop the bonnet, inspect what’s inside, and refer to the owner's manual for part names. Flashcards and online quizzes can also make learning more interactive and fun.
Another effective method is to watch educational videos or tutorials that visually demonstrate each part in action. Pairing words with images can accelerate your understanding more than text alone.
Additionally, frequent visits to car shows or dealerships where you can ask questions and physically observe various components can reinforce your knowledge. Many UK car clubs also offer hands-on workshops for newcomers keen to dive deeper.
Finally, try talking with professionals like mechanics or car enthusiasts. Conversations can expose you to practical insights and real-life scopes that no manual can offer.
Final Thoughts
Building up your knowledge of car parts not only makes you a more informed consumer but also enriches your confidence, whether negotiating repairs, maintenance, or even vehicle purchases. It’s especially beneficial if you’re a DIY enthusiast, a tradesman offering services related to car maintenance, or a designer incorporating automotive themes into your projects.
Understanding the anatomy of a vehicle empowers you to better maintain it, saving time and money while enhancing safety. As you continue to explore and learn, you’ll find that cars aren't just machines — they are marvels of engineering worth appreciating in detail.